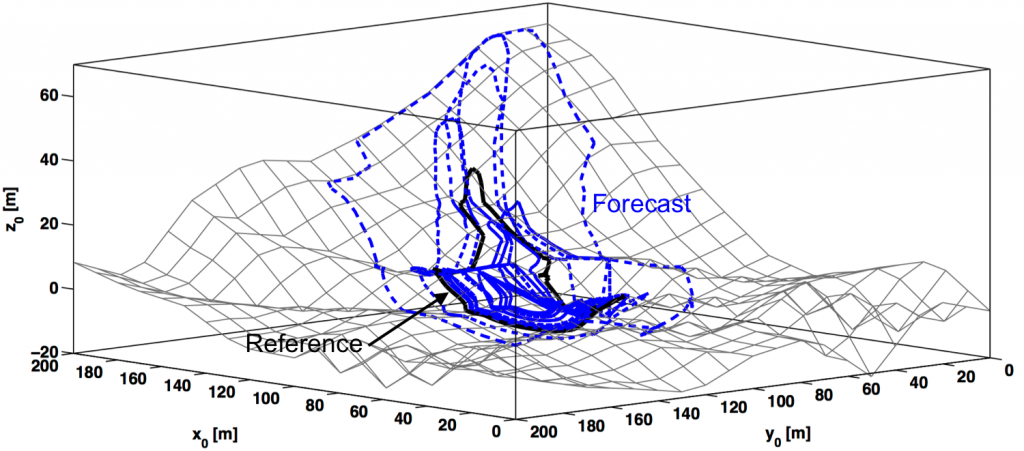
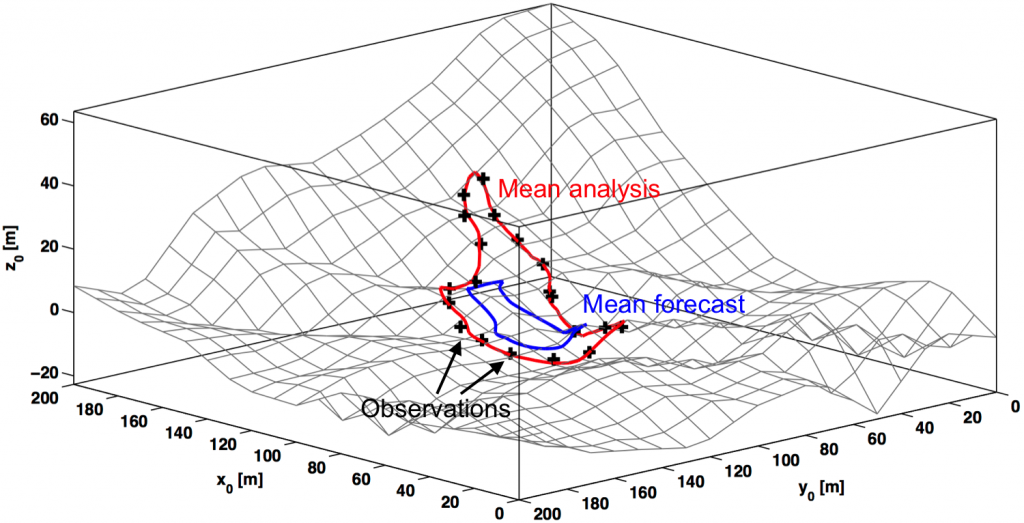
The FireFly data-driven modeling system has recently been extended to cases of fire propagation with complex terrain topography. Still, the EnKF formulation is maintained by projecting the fire front locations on the horizontal plane. The efficiency of the EnKF algorithm (state estimation approach) is illustrated on an anisotropic case of wildfire spread subject to moderate wind conditions. An ensemble of forecasts is produced based on assumed uncertainties in a subset of rate of spread model parameters, for instance in the fuel moisture content and in the wind properties.
Due to uncertainties in the rate of spread model parameters and the presence of heterogeneous terrain topography, the shape of the simulated fire fronts significantly varies between the members. The state estimation approach is able to retrieve an accurate estimation of the fire front location, in spite of the high levels of uncertainties in the prior information and the complex terrain topography.
→ Rochoux et al. (2014, VII International Conference on Forest Fire Research)

